Liabilities
Definition
A liability is “a probable future sacrifice of economic benefits arising from present obligations of an entity to transfer assets or provide services as a result of a past transaction or event.” As a result, liabilities reduce future cash flows, either directly or indirectly.
Some examples of liabilities that an organization could have include:
- Accounts payable
- Debt payable
- Salaries payable, etc.
Similarly to assets, liabilities can be current or noncurrent depending on when they are coming due.
The example below is pulled from UPS’s balance sheet :
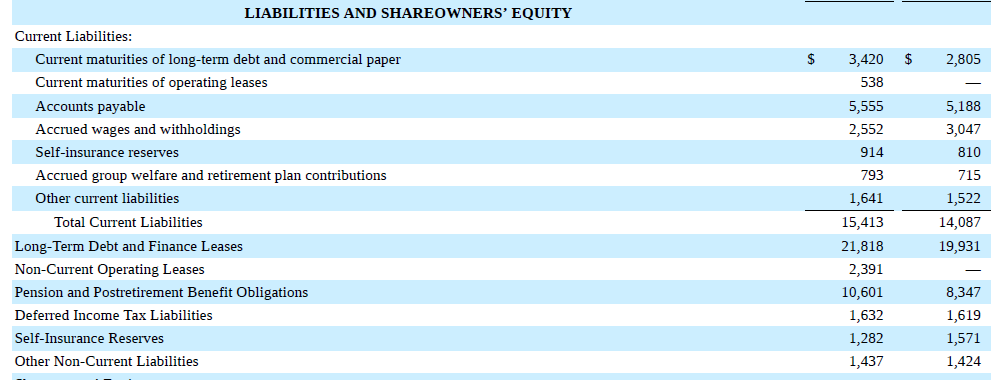
Here is the corresponding balance sheet section for Yale:

Notice the similarities and differences in these two liabilities’ section. Of course, UPS doesn’t have “Advances from federal government for student loans” and Yale does not issue “Commercial paper” (a form of borrowing), but the underlying idea of everything listed as a liability for either entity - there is a probable future sacrifice that is an obligation and it arose from some past transaction or event.